Isolating web applications protects enterprise networks from third-party access risks and threats
In the late 2000s and early 2010s, people had multiple personalities when it came to their devices. On one hand, their Blackberry pinged with email notifications from work. On the other hand (literally), their fingers left prints on the touchscreen of a new iPhone. Companies recognized that employees preferred using personal devices, which typically featured the latest technology and were customized to their preferences.
While this realization spurred “bring your own device” (BYOD) to become mainstream, the widespread adoption of unmanaged devices in an enterprise environment also brought about significant challenges, particularly in terms of security and data management. But now, under the watchful eye of a web application security solution, unmanaged and BYOD devices can access corporate applications without the risk of compromising privileged data.
Unmanaged and BYOD security risks
Modern businesses have incorporated public and private cloud applications into their daily operations. This allows employees and third-party contractors to access applications from personal or private devices, including home computers, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. While sanctioning BYOD and unmanaged devices has led to lower capital costs, engaged employees, and increased efficiency, unmanaged devices often lack the high-security standards organizations require to protect their applications and data. This leaves businesses at risk of:
- Malware infections that can spread to other applications and networks
- Targeted phishing attacks through user credentials
- Exfiltration of sensitive data using techniques such as clipboarding
- Lateral movement through the network
- Data breaches when a device is lost or stolen
Aside from the IT headache following any of these scenarios, a data breach can leave companies grappling with legal and liability issues, reputational damage, and full stops on operations.
How to control access from unmanaged devices
In the past, web application security for BYOD was typically addressed using mobile device management (MDM) or mobile application management (MAM) solutions. To access corporate applications from a personal or unmanaged device, users had to install a client that created a sandboxed environment when accessing corporate apps. This was often accompanied by a signed agreement that said if the device was lost, the company could wipe all its data, including personal information such as photos.
Although MDM, MAM, and other network access control solutions are still used in some instances of BYOD to give users access to certain parts of the network, isolation tactics are a more secure, cost-effective and modern approach.
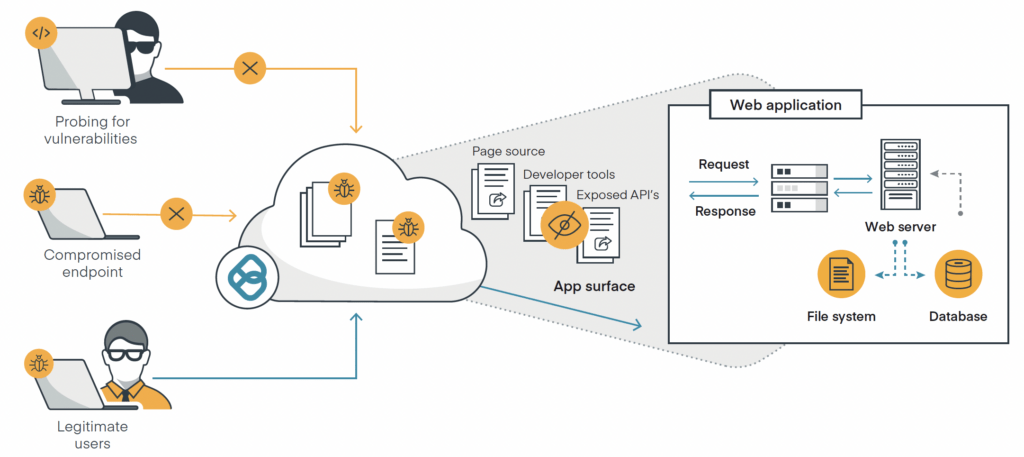
Leveraging RBI for web application isolation
Remote browser isolation (RBI) is the backbone of web application isolation (WAI) security. RBI protects businesses from web-based threats by creating a digital air gap that isolates users’ devices and activity. Here’s how it works for application security:
When a remote user on an unmanaged device opens an application through the company portal, access is automatically routed to a virtual browser in the cloud. The login will be refused if a user attempts to access the application directly, even with their legitimate username and password.
Once the user has access to the application, all content sent from their device to the application is isolated within a container. Only content rendered safe is sent from the container back to the application on the device, where users can interact just as they would with native web content. Any malware sent from the device remains in the container until it is destroyed, preventing it from reaching the enterprise web application.
Within the container, granular policy-based controls restrict content views, uploads, downloads, and clipboarding functions for certain users or groups. Content is scanned with data loss prevention (DLP) to safeguard against accidental exposure of sensitive data, and permitted uploads are sanitized within the container using content disarm and reconstruct (CDR) technology. If malware is found, it is stripped out before the attachment is reconstructed with the desired functionality intact and uploaded to the application.
How organizations benefit from clientless web application isolation
For remote employees and contractors, clientless web application isolation technology means they can access necessary corporate applications seamlessly — they simply open their browser and click. The behind-the-scenes protection is transparent to users and provides benefits to the enterprise, including:
- Providing a safeguard against the exposure of confidential information and PII
- Quick user onboarding
- Simple cancellation of user privileges when no longer needed
- Policy management across the enterprise from a single management console
Determining web application security needs for your enterprise
Research from Verizon found that web application attacks are involved in more than a quarter of all breaches, making them the second most common pattern of attack. If companies can get a handle on web application security, they’ll fortify a large portion of their security posture. But securing vulnerable applications through isolation isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution.
Each unique organization must analyze its risk profile to determine if web application isolation is the best investment to improve its security posture, or if WAI is only one ingredient in a larger zero trust recipe. Although regulatory and compliance restrictions may guide these decisions in certain industries, a comprehensive approach to security with multiple solutions in place to provide defense in depth is an effective risk management strategy.
