This month’s Threat Intelligence Report, published by Cradlepoint's Threat Research and Analysis (TR&A) Team, covers vulnerabilities in Telit Cinterion cellular modems (remote code execution) and ThroughTek Kalay's SDK (unauthenticated admin access). It also provides an overview of attacks on water utilities from Q1 2023 to present.
Cinterion Vulnerability has a wide impact on IoT/OT devices (CVE-2023-47610)
Security researchers at Kaspersky have discovered vulnerabilities in Telit Cinterion cellular modems that allow unauthenticated, remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via crafted SMS messages (CVE-2023-47610). Telit is a global provider of cellular modems for industries with dispersed IoT and OT devices. Telit modems are embedded in other vendor products, making it difficult for an organization to know whether this vulnerability impacts them. Cellular modems frequently use SMS for backup communication and remote management. Security researchers recommend limiting SMS features, which may not be feasible because it would impact operational requirements. The impacted modem models are BGS5, EHS5/6/8, PDS5/6/8, ELS61/81, and PLS62. See the KLCERT-23-018: Telit Cinterion (Thales/Gemalto) modules for more details. Buffer Copy without Checking Size of Input vulnerability | Kaspersky ICS CERT
TR&A Comments: At the time of publication, there are no reports of in-the-wild exploits or proof-of-concept code for CVE-2023-47610, and a patch was released by the vendor Telit. However, state-sponsored threat actors APT 28 and Volt Typhoon have increased attacks on internet-connected IoT/OT devices, which may result in the quick development of exploit code. These threat actors have exploited similar vulnerabilities to conduct espionage and disrupt operations.
Cradlepoint solutions for proactive defense: Using a private cellular network to reduce the attack surface effectively mitigates this vulnerability. Remove internet access to these devices while maintaining connectivity using Cradlepoint’s NetCloud Private Networks Mobility Gateway. Restricting access to vulnerable devices can reduce the threat while devices are patched.
ThroughTek Kalay SDK vulnerabilities (CVE-2024-22 to 24)
Security researchers at Bitdefender found four vulnerabilities in the SDK of the ThroughTek Kalay IoT management platform — security camera vendors, including D-Link, TP-Link, and Zmodo, partner with ThroughTek to provide customers with remote management of internet-connected IoT devices. Using the SDK vulnerabilities in sequence would allow an attacker to gain remote unauthenticated administrator access to a device using the leaked device AuthKey, establishing a DTLS session using a blank secret value, and gaining root access from a stack-based buffer overflow. The vulnerabilities’ CVSS scores range from 4.2 to 8.1. However, it is the linking of the vulnerabilities in an attack lifecycle that increases the overall risk. Vendors of impacted devices have published updated versions of firmware and SDKs. For more details, see the whitepapers at https://www.bitdefender.com/blog/labs/notes-on-throughtek-kalay-vulnerabilities-and-their-impact/
TR&A Comments: Exploiting the AuthKey vulnerability requires local network access, but the other vulnerabilities do not. At most risk are security devices that are physically accessible, such as traffic cameras with controls located in a nearby secured box. Breaching the secured box allows attackers to access the camera's local network and begin lateral movement to spread malware or compromise additional devices.
Cradlepoint solutions for proactive defense: Cradlepoint’s Secure Connect implements zero-trust networks by default. Denied inbound internet access and explicit access policies would mitigate the ability of attackers to access the device from the internet and reduce the impact of lateral movement.
Water utilities
The EPA issued an enforcement alert on May 20, 2024, to inform community water utilities of the increasing number of cyberattacks impacting utility operations. Enforcement alerts are issued when threats increase, prompting additional and immediate action. The EPA inspects water utilities as part of the Safe Drinking Water Act section 1433. They have recently reported that inspected systems have critical cybersecurity vulnerabilities, such as default passwords that have not been updated and shared logins. For more details, see EPA Outlines Enforcement Measures to Help Prevent Cybersecurity Attacks and Protect the Nation’s Drinking Water | US EPA
TR&A Comments: Cradlepoint’s TR&A Team has been tracking reported water utility attacks since early 2023 to report on techniques for initial access and lateral movement from threat actors such as People’s Republic of China (PRC) state-sponsored cyber actor Volt Typhoon and Russia’s ATP 28 Cozy Bear. The image below shows an increasing number of reported attacks, and most likely more go unreported. Water utility advisories have been published in the past year, and the EPA enforcement alert continues to raise the alarm of increasing threats.
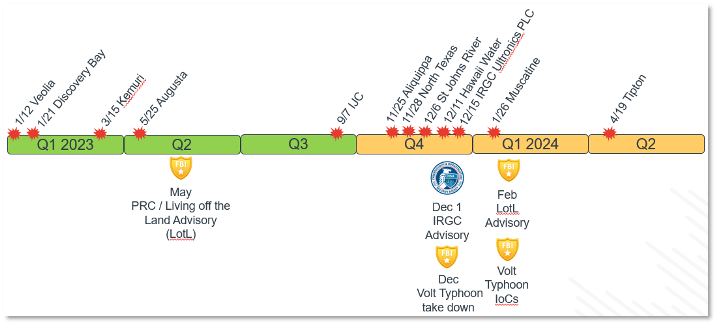
Figure 1. Water utility compromise timeline
Cradlepoint solutions for proactive defense:
- PRC threat actors are known to target perimeter devices for initial access. Use Cradlepoint’s Secure Connect to obfuscate the device's WAN interface connected to the internet while providing secured remote administrative access.
- APT 28 Cozy Bear uses “living off the land” (LotL) techniques, which are attacks using system tools installed by default or for common network administration tools. Use Cradlepoint’s Secure Connect to implement explicit trust policies to limit lateral movement using LotL techniques.
High-risk vulnerabilities Cradlepoint solutions would mitigate
The vulnerabilities listed were published or added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog in May, are actively exploited, and are relevant to the technology used by Cradlepoint target industries.
ZTNA: Network segmentation, Policy based access
| Product | Criticality 1-10 | Impact | Industry | Active Exploits? | CVE |
| NextGen Healthcare | 9.8 | NextGen Healthcare Mirth Connect is an open-source data integration platform widely used by healthcare companies. Versions before 4.4.1 are vulnerable to unauthenticated remote code execution. | Healthcare | Yes | CVE-2023-43208 |
| D-Link | 7.5 | D-Link DIR-605 routers contain an information disclosure vulnerability that allows attackers to obtain a username and password by forging a post request to the /getcfg.php page. | Multiple | Yes | CVE-2021-40655 |
| D-Link | 6.8 | D-Link DIR-600 routers contain a cross-site request forgery (CSRF) vulnerability that allows an attacker to change router configurations by hijacking an existing administrator session. | Multiple | Yes | CVE-2014-100005 |
Remote Browser Isolation (RBI)
| Product | Criticality 1-10 | Impact | Industry | Active Exploits? | CVE |
| Chrome | 8.8 | Google Chromium V8 Type Confusion | Multiple | Yes | CVE-2024 -5274 -4947 -4761 |
| Chrome | 9.6 | Google Chromium Visuals contains a use-after-free vulnerability that allows a remote attacker to exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page. This vulnerability could affect multiple web browsers that utilize Chromium. | Multiple | Yes | CVE-2024-4671 |
Web Application Isolation (WAI)
| Product | Criticality 1-10 | Impact | Industry | Active Exploits? | CVE |
| Apache | 7.5 | Apache Flink contains an improper access control vulnerability that allows an attacker to read any file on the local filesystem of the JobManager through its REST interface. | Multiple | Yes | CVE-2020-17519 |
