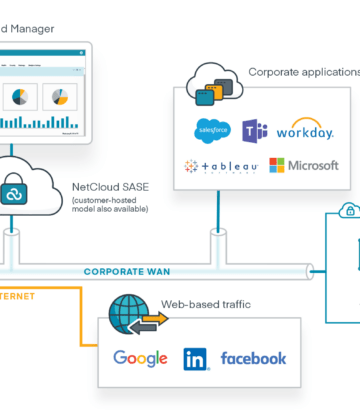
Harmonize SD-WAN and 5G for optimization of traffic flows
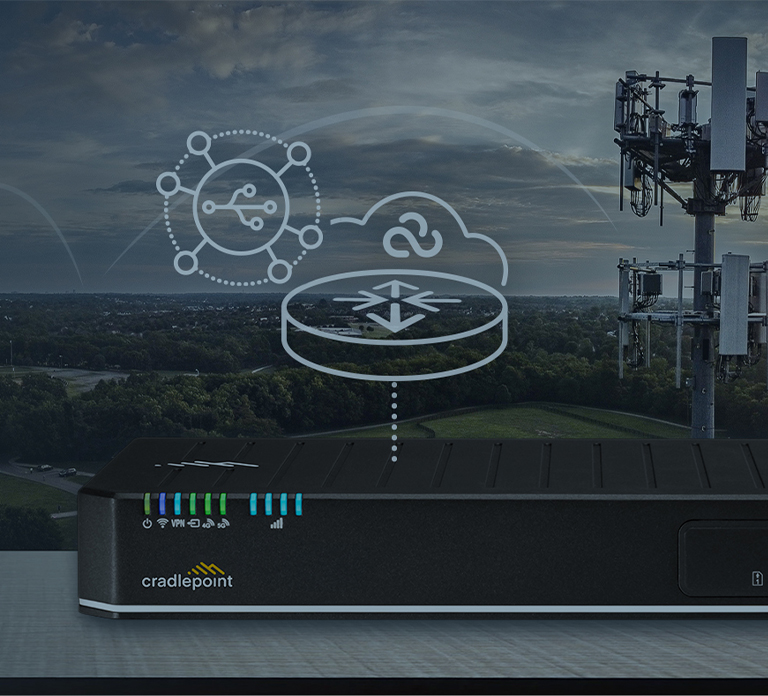
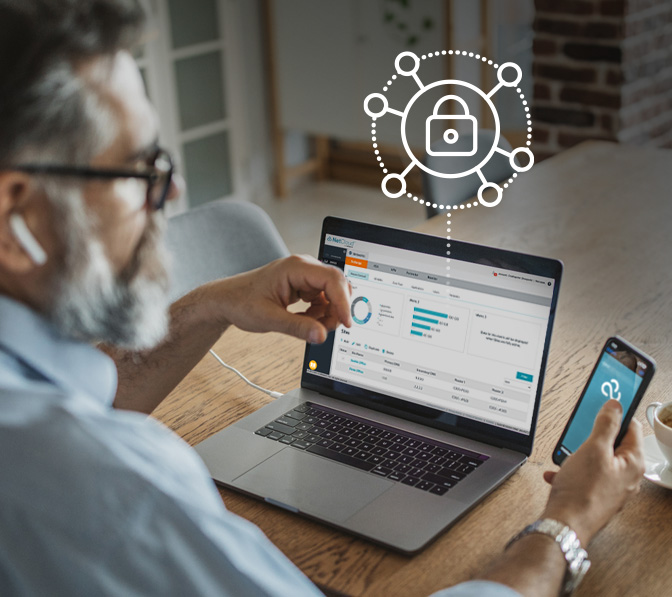
SD-WAN has helped many businesses improve network performance, simplify management, and reduce costs in fixed site and hybrid work environments. But even the best technologies must evolve. Next up? SD-WAN must move beyond wired-centric features to accommodate the proliferation of technologies in vehicles, stores, offices, and IoT — all interconnected by 5G. With zero trust SD-WAN, enterprises can deploy a simpler, more secure SD-WAN solution that amplifies the 5G experience and simplifies the transition from wired to Wireless WAN.