Hybrid WAN and dual modems for fixed sites
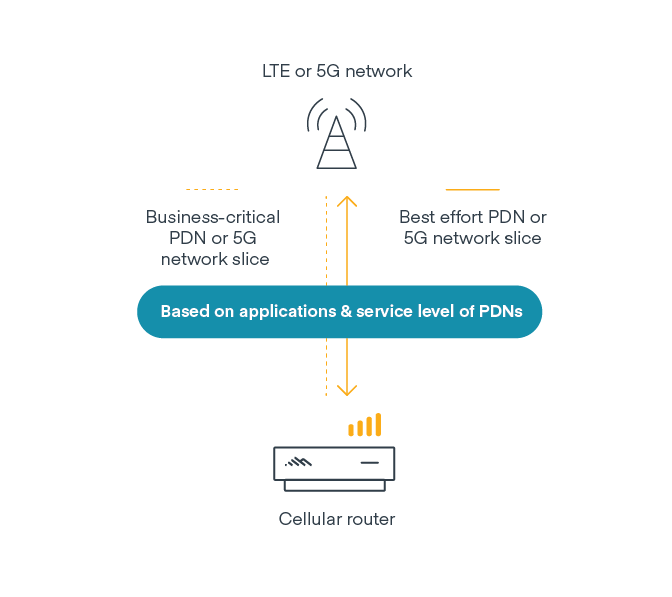
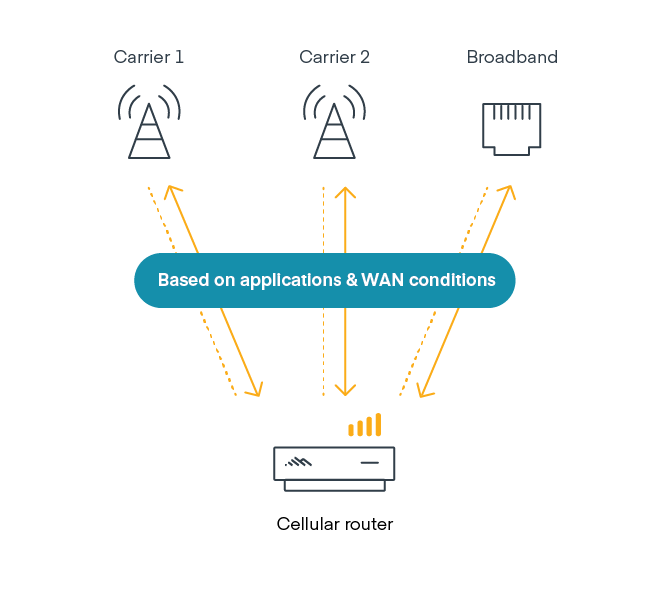
Organizations with lots of widely distributed stores or branch offices can meet most of their edge networking needs through one solution by deploying a hybrid WAN router that includes cloud-managed SD-WAN features; multiple types of WAN connections; two cellular modems; Wi-Fi; and zero trust network access (ZTNA) technologies. This is the most efficient and scalable way to support SD-WAN capabilities and 5G or LTE amid a rapid expansion of fixed sites.