Each month the TR&A team publishes a threat intelligence report to inform organizations about relevant changes in the threat landscape. This report covers events during July 2024.
At a glance
- Black Basta developed increasingly stealthy malware
- DDoS attack overwhelmed Microsoft cloud services, challenging cloud providers
- Infostealer and loaders — new and improved malware variants, and novel social engineering lures
- July trend of known exploited vulnerabilities and initial access of data breaches
- High-risk vulnerabilities that Cradlepoint solutions would mitigate
Our Views on Recent Attacks:
In the past month, a denial-of-service attack impacted Microsoft cloud platforms, which could be the culmination of the botnets threat actors have been developing for the past two years. Threat actors remained focused on info-stealers and loader malware for initial access, as evidenced by new variants. Application vulnerabilities continued to expand organizations' attack surfaces, accounting for 60% of all known exploited vulnerabilities. Lastly, data breaches impacted 18.6 million individuals, roughly equivalent to the population of New York state.
Black Basta
Walmart’s Cyber Intelligence Team observed a new PowerShell-based malware used to launch reconnaissance activities and download additional malware. The malware was linked to Black Basta due to other software observed in the attack lifecycle commonly associated with the group. The malware used sophisticated obfuscation techniques such as anti-VM checks, code obfuscation, and well-encrypted command and control communications. For more details, see https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/walmart-powershell-backdoor-zloader/ and https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/unc4393-goes-gently-into-silentnight
TR&A Comments: The use of PowerShell in new malware aligns with CISA reports highlighting the growing adoption of “living off the land” techniques by threat actors. This trend may also signify a shift toward leveraging scripting languages in malware to evade security controls. Defenders are advised to minimize the use of administrative tools, restrict access to systems that run these tools, and implement behavior-based detections to counter script-based attacks.
Cradlepoint solutions for active defense: NetCloud Secure Connect implements zero trust policies by default. Zero trust uses explicit trust policies that limit reconnaissance and lateral movement tactics.
Challenges of an emerging DDoS attack technique
OVHCloud, a leading European cloud service provider, recently reported a record-breaking DDoS attack characterized by an unprecedented packet rate, leveraging compromised MikroTik core routers. Unlike typical DDoS attacks that rely on numerous small devices to generate traffic, this attack utilized core routers to produce significantly higher volumes of attack traffic. Microsoft also experienced a substantial DDoS attack that disrupted their cloud services.
While the success of the attack was due to both the increased traffic rate and a misconfiguration of Microsoft’s mitigation controls, high-volume core routers also could have been used to generate an attack powerful enough to impact a leading global cloud services platform. For more details, see the OVhcloud blog. https://blog.ovhcloud.com/the-rise-of-packet-rate-attacks-when-core-routers-turn-evil/
TR&A Comments: In the past year, botnet infection rate and malware sophistication have increased. Since 2022, there have been at least five critical vulnerabilities reported in MikroTik routers. However- intelligence reports indicated that SOHO and small sized routers were the target. The success of core routers generating record-breaking DDoS traffic may result in a shift of threat actors targeting core routers. Defenders are recommended to ensure the security of their core routers’ internet accessible attack surface and limit remote administration from all networks.
Cradlepoint solutions for active defense: Attack surface reduction using a combination of secure remote access and zero trust network architecture can eliminate the opportunity for a threat actor to attack network devices. Cradlepoint’s Zero Trust Private Access and Zero Trust Internet Access allow an organization to secure remote access to device administration applications, removing the need for VPN devices and software.
New info-stealer and loader malware
The table below lists info-stealer and loader malware improvements observed in June 2024. This month there was at least one upgraded version of existing malwares, and four new malware variants.
Updated malware variants
| Variant | Improvements | Threat Actors |
| Fake IT support site for Windows errors | User runs malicious PowerShell script, which installs Vidar stealer. | SEO poisoning. YouTube channel with fake reviews. |
New malware
| Variant | Improvements | Threat Actors |
| HappyDoor | Data gathering (cookie theft and browser screenshot capture) and secondary payload execution features. | Kimsuky |
| Caesar Cipher Skimmer | Hijacks checkout to steal credit card data. Uses obfuscated strings and a Caesar Cipher technique to hide its malicious domain from security monitoring controls. Deployed across multiple content platforms. |
Unattributed |
| dllFake infostealer | Software supply chain attack replacing trojanized software downloads on the valid vendor site. | Unattributed |
| Jellyfish loader | Sends system information to C2 server upon initial infection. Encrypted C2 communication for further malware downloads. |
Hades Group (low confidence) |
New campaigns using social engineering
Five new campaigns using social engineering lures were observed this month. Campaigns are a focused effort by one or more threat actors toward a common objective. Info stealer and loader malware downloads continued to be the leading objective. The rise in registered domains mimicking popular product brands and fake positive user reviews may be in preparation for the U.S. holiday season, a time when online shopping surges, providing threat actors with an opportunity to lure users to malicious websites.
The impact of stealers is the loss of data such as credentials, browser extension information, clipboard contents, and keyboard stroke capture. This data is exfiltrated and commonly used in future attacks. Loaders establish initial access on a user’s system and then communicates with the command-and-control server to download additional malware.
| Campaign | Technique | Tactic |
| Fake IT support site for Windows errors | User runs malicious PowerShell script, which installs Vidar stealer. | SEO poisoning. YouTube channel with fake reviews. |
| New dedicated software websites, verified social media profiles, promotional videos, user reviews | User downloads software, which contains the FakeBat loader. | Typo-squatting. Malvertizing on legitimate platforms. PowerShell scripts. |
| eBook torrent downloads | User downloads file, which contains ViperSoftX stealer. | Advertising free access to eBooks on legitimate sites. |
| Download Crowdstrike hotfix | User extracts zip file, which installs HijackLoader or Lumma stealer. | Phishing. Impersonation phone calls. Selling “automated repair scripts” on legitimate platforms. |
| Spam email campaign leveraging legitimate M365 tenants | Emails passed DKIM and SPF checks, so delivered to inboxes without being flagged as spam. | Exploited vulnerability in Proofpoint email protection service to perform Echospoofing. |
TR&A Comments: As social engineering techniques become more sophisticated, users will find it more difficult to differentiate between legitimate and malicious content. Additionally, improvements in loader and info-stealer malware variants will challenge Defenders to maintain detection of these attacks.
Cradlepoint solutions for active defense: Cradlepoint’s Zero Trust Internet Access creates secure virtual environments for user sessions, effectively countering information stealer downloads and browser vulnerability exploits. Isolation inserts a digital air gap between web content and user devices. Each user browsing or application session is executed in an isolated cloud container. Only a safe virtual stream of the rendered website is sent in real time to the user’s browser. This means that all active code remains isolated in the cloud, so malware can never reach the user’s device or the network. In addition, suspicious sites such as spoofed login pages can be opened in read-only mode so that users cannot enter credentials.
Vulnerability and Data Breach Trends
Threat actor targets
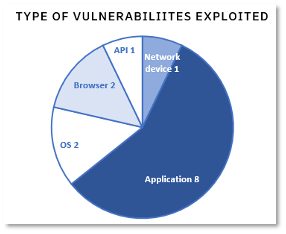
Application vulnerabilities lead the type added to the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerability list. This is consistent with TR&A’s findings in our Q3 Threat Intelligence Report. Application vulnerabilities are expected to remain a target from attackers, especially to gain initial access from internet-facing applications.
DB and initial access techniques
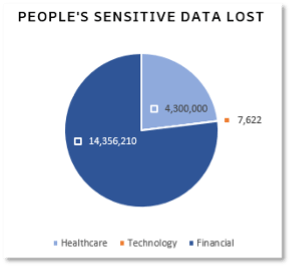
Five data breaches included sensitive personal information, impacting a total of 18.6 million people. Three organizations were financial, with one each in Healthcare and Technology. Three threat actors were named: 888, LockBit and AlphV. The initial access techniques for those cyber gangs and affiliates are:
| Threat actor | Initial access techniques |
| 888 (name used in a dark web marketplace) | As of publication, no threat actors have been associated with this account on the dark web marketplace. |
| LockBit | External Remote Services (T1133) Valid Accounts (T1078) |
| AlphV | Exploit Public Facing Applications (T1190) External Remote Services (T1133) Valid Accounts (T1078) |
High-risk vulnerabilities that Cradlepoint solutions would mitigate
The vulnerabilities listed below are actively exploited and relevant to the Cradlepoint technology used by many industries, including vulnerabilities published or added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog in July 2024.
| Product | Criticality (CVSS 3.0) | Impact | Industry | Exploited? | CVE |
| OpenSSH (RegreSSHion) | 8.1 High |
An unauthenticated remote code execution in OpenSSH’s server (sshd) that grants full root access. | Multiple | Yes | CVE-2024-6387 |
| D-Link DIR-859 router (End of Life) | 9.8 Critical |
HTTP management interface vulnerability allows path traversal for remote unauthenticated execution. | Multiple | Yes | CVE-2024-0769 |
| Rejetto HTTP File Server | 9.8 Critical |
Template injection vulnerability allows remote unauthenticated user to execute commands on the system. | Multiple | Yes | CVE-2024-23692 |
| OSGeo GeoServer Geo Tools | 9.8 Critical |
API unsafely passes names to the commons-jxpath library, allowing remote code execution. | Multiple | Yes | CVE-2024-36401 |
| SolarWinds Serv-U | 7.5 High |
Directory transversal vulnerability allows unauthenticated read access to sensitive files. | Multiple | Yes | CVE-2024-28995 |
| Acronis Cyber Infrastructure (ACI) | 9.8 Critical |
Allows threat actors to execute arbitrary code remotely due to the use of default passwords. | Multiple | Yes | CVE-2023-45249 |
| ServiceNow | 9.8 Critical |
Input validation vulnerability allows an unauthenticated user to remotely execute code within the context of the Now Platform. | Multiple | Yes | CVE-2024-5217 CVE-2024-4879 |
| Product | Criticality (CVSS 3.0) | Impact | Industry | Exploited? | CVE |
| Microsoft Internet Explorer: Versions 6-8 | 8.8 High |
Use-after-free vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via a crafted web site. | Multiple | Yes | CVE-2012-4792 |
For more monthly threat intelligence reports, please visit our threat intelligence blog. If you would like to speak with a Cradlepoint solutions person, please contact us by clicking on “Cradlepoint Chat” on our website.
