Each quarter, the Cradlepoint Threat Intelligence and Analysis (TR&A) Team researches and informs its customers about the threat landscape, providing threat intelligence that also informs Cradlepoint’s product design and ability to respond to active threats. This report covers events from October through December 2023.
Our Views on Recent Attacks
- Patching lag caused increased risk due to same day exploits for high-risk vulnerabilities
- Initial access techniques in top three data breaches
- SOHO router vulnerabilities exploited for lateral movement into organizations
- 2024 Election Voting System Security
More patches + less time = increasing risk
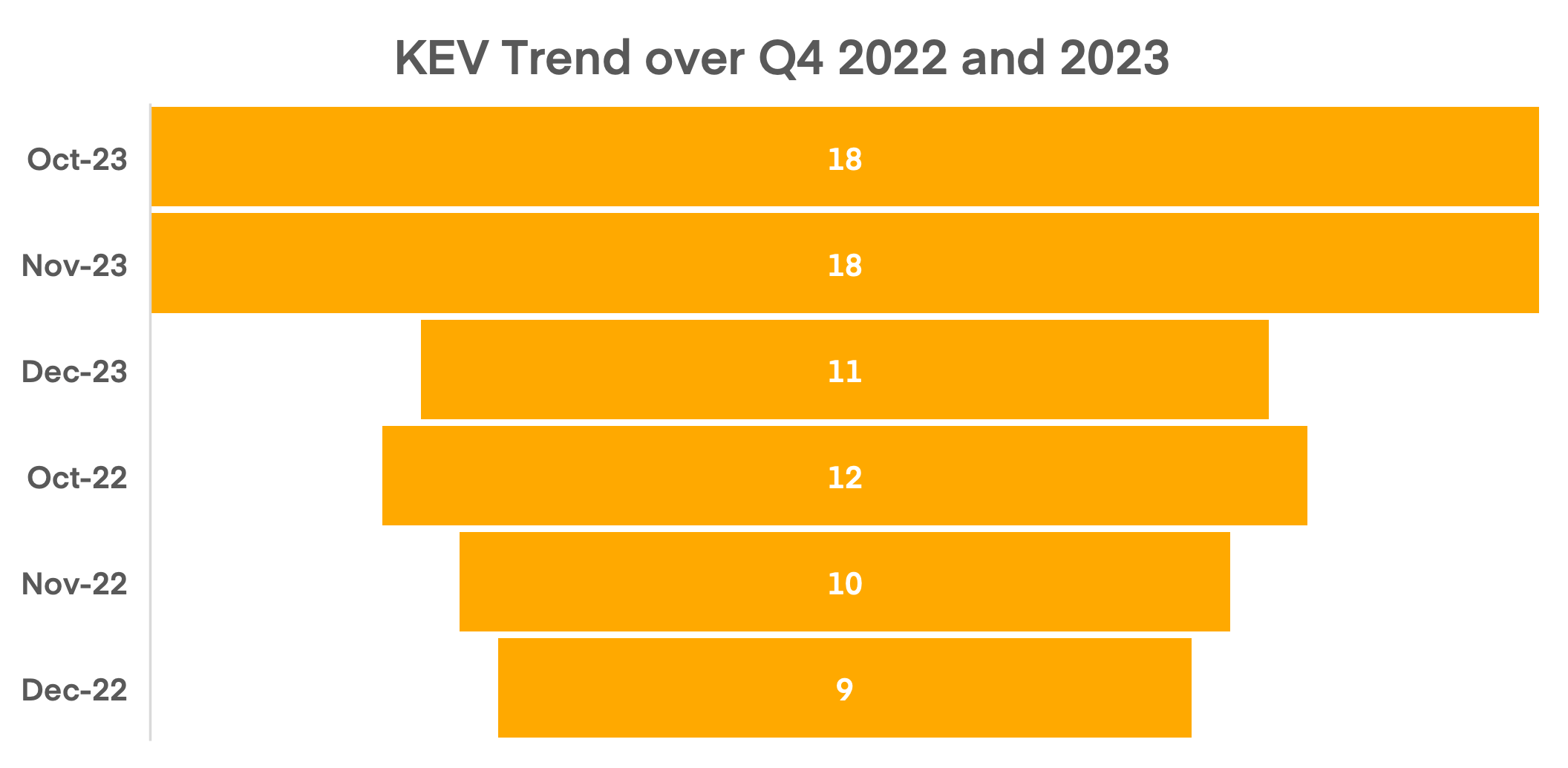
Qualys security researchers found that 25% of high-risk CVEs had exploits published on the same day as the announcement. Additionally, CISA’s Associate Director for Capacity Building in Cybersecurity, Michael Duffy, warned of the rapid increase in zero-day activity in 2023[1] and forecast the same trend into 2024. Compounding the urgency to patch high-risk CVEs, CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) data showed a 30% rise in exploited vulnerabilities in Q4’23 compared to 2022. This surge in high-risk vulnerabilities and same day exploits significantly increased pressure on organizations to patch within 24 hours of a release. For more details, read the Qualys blog.
TR&A Comments: Organizational risk is rising due to patching lag and quickly exploited high risk vulnerabilities and requires additional defenses to mitigate the threat of zero-day exploits. Firewall and VPN perimeter defense are no longer effective, as proven by these increasingly successful attacks. In some instances, patches for critical vulnerabilities aren’t available from the vendor in a timely manner or mitigation requires an upgrade. Given these challenges, limiting internet access to applications that handle sensitive data or connect to trusted networks is crucial to reducing organizational risk.
Cradlepoint solutions for proactive defense against zero day attacks:
Remote Browser Isolation (RBI) and Web Application Isolation (WAI) creates secure virtual environments for user sessions, effectively countering zero-day and rapidly exploited vulnerabilities. Isolation inserts a digital air gap between web content and user devices. Each user browsing or application session is executed in an isolated cloud container. Only a safe virtual stream of the rendered website is sent in real-time to the user’s browser. This means that all active code remains isolated in the cloud, so malware can never reach the user’s device.
Initial access techniques for top 3 data breaches in Q4’23
In Q4 there were 685 data breaches[1]. The initial access techniques used in the top three breaches were stolen credentials, exploiting vulnerable applications on the internet and system misconfiguration:
| Technique | Records exposed | Threat Actor | Attack Type |
| Opportunistic reconnaissance for misconfigured databases on the internet | 1.5 billion | Not reported | Data exfiltration |
| Zero-day SQL Injection vulnerability | 18.6 million | CL0P | Data exfiltration |
| Stolen valid credentials, aka credential stuffing | 13 million | Alphav/BlackCat | Ransomware |
The trend in compromising valid credentials predominantly involved phishing and the increased use of web-browser credential stealers. These credential stealers masqueraded as legitimate updates or browser plugins, but were malware designed to steal browser-stored credentials, cookies, and session tokens. However, the most significant breaches were due to compromised internet-facing systems. A misconfigured database server at Real Estate Wealth Network led to the exposure of 1.5 billion records, the largest number of records ever exposed in a single incident. And as investigations into the zero-day exploit in MOVEit software's SQL database progressed, the tally of data loss continued with over eighteen million records reported this quarter. Visit VPN Mentor for more information about the Real Estate Wealth Network breach.
TR&A Comments: For both the CL0P and Real Estate Wealth Network breaches, the attack required a publicly available internet-facing resource–a file transfer website or a database. In both cases, the targeted resources were internet-facing to facilitate third-party data access.
Cradlepoint solutions for protecting systems storing sensitive data:
Cradlepoint’s Web Application Isolation solution has DLP functionality to stop PII and specific sensitive data from being exported during a browser session. Policy-based controls limit website content and user actions based on user type. Similarly, our Remote Browser Isolation solution uses DLP to protect users from phishing attacks threat actors use to steal credentials. Browser content can be restricted to disable users’ ability to input credentials using policy-based controls.
[1] IT Governance report links: October, November, December
SOHO Botnet malware positioned to expand attacks
Throughout 2023, Microsoft, Talos, and CISA observed that attackers exploited vulnerabilities in end-of-life SOHO routers to establish covert operations. These compromised routers were used for data transfer from victim networks, establishing command and control servers, and circumventing geo-fencing by using local IPs. The exploits provided root access to routers, enabling attackers to install tools, conduct man-in-the-middle attacks, and redirect traffic to malicious sites. More recently, LAN reconnaissance tools were detected on compromised routers, hinting at potential future attacks on internal organizational devices. For more details, read the Lumen blog.
TR&A Comments: Traditionally, the network perimeter was well-defined and relatively static, often protected by firewalls and other security devices. However, with the number of zero-day attacks on internet facing network devices cybersecurity discussions should redefine the point of defense for routers, firewalls, VPN gateway and other internet connected devices. Security measures should now focus on securing traffic upstream of the logical network boundary. Traffic to these devices should be defined, inspected, and ideally authenticated to reduce the opportunity for a threat actor to exploit vulnerabilities. Consider a private cloud solution which mitigates threats upstream from internet accessible network devices.
Cradlepoint solutions security for the edge:
A combination of Zerto Trust WAN Security and Zero Trust Web Security allows an organization to proactively defend against zero-day attacks and provide clientless zero trust access to internet-available web applications. Our 5G zero trust WAN is built with security designed in, operates on an invitation-only basis, and hides all IP addresses, thereby making each site, asset, and application in the WAN dark to each other and to the outside world.
Election voting system security in 2024
Local governments will be establishing IT infrastructure to support polling sites for the coming US presidential election. The ability to protect against fraud and to demonstrate system integrity s critical to the legitimacy of the count. Both hacktivist and nation state actors will target the people, technology, and physical assets to potentially manipulate the elections results or perception of integrity. Polling sites are a potential target of those actors: they are geographically dispersed and may not have the defense in depth security controls of a stationary site. Additionally, polling sites will require a variety of devices to be network-connected, including voting systems, poll worker laptops for voter verification, and potentially polling site workers’ personal devices, all of which require different levels of security control. A defense-in-depth cybersecurity strategy that ensures no public internet connection for networks hosting critical election technology is crucial for mitigating initial access techniques. For more details, visit CISA.gov and electiondefense.org.
Cybersecurity experts at Mandiant highlight risks to election system data integrity from internet attacks, supply chain, and third-party vulnerabilities, including threats to voting machine software and vendor support access. Since the successful SolarWinds supply chain attack in 2020, actors have rapidly increased software supply chain attacks[2], targeting open source and commercial software for malicious activities. Actors use the compromised software to spread disruptive malware to other devices on a trusted network or provide a backdoor to actors if the device is connected to the internet. For more details, see the Q4 2023 Election Assistance Committee intelligence briefing.
TR&A Comments: The combination of highly motivated threat actors, the high-value target voting systems, and varying security controls at dispersed polling sites should motivate election boards to consider stricter than normal security controls, especially internet access for any device at the polling site.
Cradlepoint solutions for secure cloud over 5G solutions:
Isolating a geographically dispersed infrastructure usually requires VPN over wired connections from telco providers which are expensive, require a long provisioning time, and are inflexible when there are logistical changes. Cradlepoint’s NetCloud Exchange Secure Connect over 5G solution using SD-WAN and NetCloud Exchange Service Gateway can secure voting systems by:
- Eliminating vulnerable VPNs, which expose IP ports and offer network-level connections to corporate infrastructure and the internet. Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) would enable granular user-level access to polling data aggregation systems. On micro-segmented networks, even legitimate users and systems can access only the applications they need. Policy-based least privilege access could also limit the information that users have access to.
- Establishing a “connect-and-go zero trust network” that provides elevated security and simplified, and speedier setup in comparison to VPNs through intuitive WAN orchestration.
- Using SD-WAN cellular Intelligence to provide WAN resilience and prioritization.
All Quarterly Cradlepoint Threat Intelligence Reports can be found on the Cradlepoint blog.
